【笔记】Vue Element+Node.js开发企业通用管理后台系统——Vue进阶(下)
一、组件通信 provide 和 inject
<body>
<div id="root">
<Test></Test>
</div>
<script>
function registerPlugin() {
Vue.component('Test', {
template: '<div>{{message}}<Test2 /></div>',
provide() {
return {
elTest: this
}
}, // function 的用途是为了获取运行时环境,否则 this 将指向 window
data() {
return {
message: 'message from Test'
}
},
methods: {
change(component) {
this.message = 'message from ' + component
}
}
})
Vue.component('Test2', {
template: '<Test3 />'
})
Vue.component('Test3', {
template: '<button @click="changeMessage">change</button>',
inject: ['elTest'],
methods: {
changeMessage() {
this.elTest.change(this.$options._componentTag)
}
}
})
}
Vue.use(registerPlugin)
new Vue({
el: '#root'
})
</script>
</body>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
先来看一下官方文档中的说明:
类型:
- provide:Object | () => Object
- inject:Array< string > | { [key: string]: string | Symbol | Object }
详细:
- 这对选项需要一起使用,以允许一个祖先组件向其所有子孙后代注入一个依赖,不论组件层次有多深,并在起上下游关系成立的时间里始终生效。
- provide 选项应该是一个对象或返回一个对象的函数。该对象包含可注入其子孙的属性。
- inject 选项应该是:
- 一个字符串数组,或一个对象,对象的 key 是本地的绑定名,value 是:
- 在可用的注入内容中搜索用的 key (字符串或 Symbol),或
- 一个对象,该对象的:
- from 属性是在可用的注入内容中搜索用的 key (字符串或 Symbol)
- default 属性是降级情况下使用的 value
PS:provide 和 inject 主要在开发高阶插件/组件库时使用。并不推荐用于普通应用程序代码中。
示例代码解析:
- 可以说一个组件它的内部资源是私有的,子孙也不可及,通过
provide将它的属性/方法/数据/…,甚至它自身(this)暴露出去,提供给子孙后代使用:
provide() {
return {
elTest: this
}
},
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
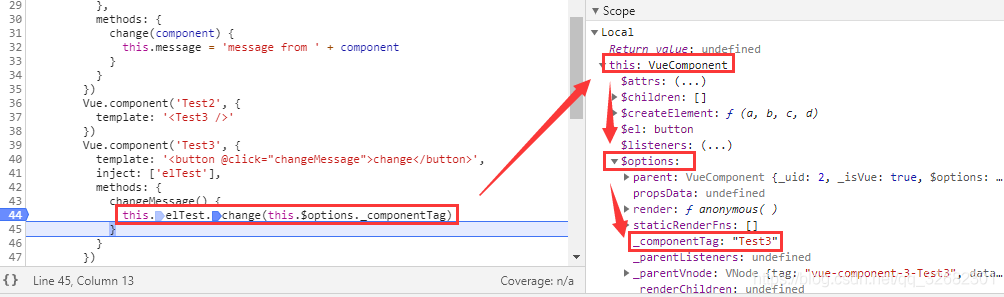
this:VueComponent(祖先组件:Test)
inject: ['elTest'],
- 1
this.elTest.change(this.$options._componentTag)
- 1
this:VueComponent(孙辈组件:Test3)this.elTest:VueComponent(祖先组件:Test)this.$options._componentTag:这里的this指的是调用change方法的this.elTest,也就是祖先组件:Test
二、过滤器 filter
官方文档:https://cn.vuejs.org/v2/api/#Vue-filter
官方文档:https://cn.vuejs.org/v2/guide/filters.html
实例:过滤器 filter
<body>
<div id="root">
{{message | lower}}
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#root',
filters: {
lower(value) {
return value.toLowerCase()
}
},
data() {
return {
message: 'Hello Vue'
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
先来看一下官方文档中的说明:
Vue.js 允许自定义过滤器,可被用于一些常见的文本格式化。
过滤器可以用在两个地方:双花括号插值和 v-bind 表达式 (后者从 2.1.0+ 开始支持)。
过滤器应该被添加在 JavaScript 表达式的尾部,由“管道”符号指示:
<!-- 在双花括号中 -->
{{ message | capitalize }}
<!-- 在 `v-bind` 中 -->
<div v-bind:id="rawId | formatId"></div>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
可以在一个组件的选项中定义本地的过滤器
或者在创建 Vue 实例之前全局定义过滤器
当全局过滤器和局部过滤器重名时,会采用局部过滤器。
过滤器可以串联:
{{ message | filterA | filterB }}
- 1
过滤器是 JavaScript 函数,因此可以接收参数:
{{ message | filterA('arg1', arg2) }}
- 1
这里,filterA 被定义为接收三个参数的过滤器函数。其中 message 的值作为第一个参数,普通字符串 ‘arg1’ 作为第二个参数,表达式 arg2 的值作为第三个参数。
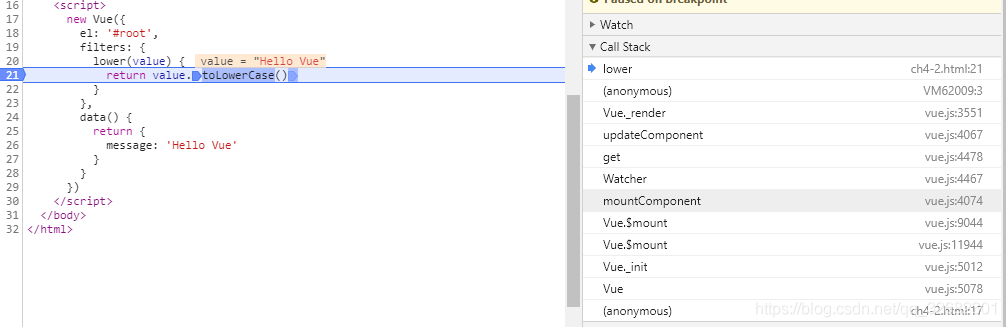
filters执行前后过程分析(by call stack):
- Vue,_init:实现vue初始化
- 在Vue.$mount中通过mountComponent实例化一个Watcher对象
- 接下来调用updateComponent方法
- 方法内执行Vue._render函数
- 函数通过对template解析
- 然后解析过程中对传进来的参数进行指定的过滤处理
- 最后将结果返回,渲染
具体解析:传送门:filter源码详解
三、监听器 watch
官方文档:https://cn.vuejs.org/v2/api/#watch
官方文档:https://cn.vuejs.org/v2/api/#vm-watch
实例:监听器 watch
Watch 用法1:常见用法
<body>
<div id="root">
<h3>Watch 用法1:常见用法</h3>
<input v-model="message">
<span>{{copyMessage}}</span>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#root',
watch: {
message(value) {
this.copyMessage = value
}
},
data() {
return {
message: 'Hello Vue',
copyMessage: ''
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
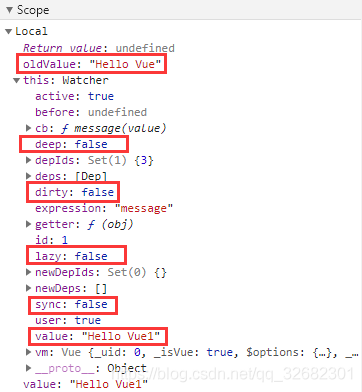
键值一体,键为message,值为message()方法
message(value) {
this.copyMessage = value
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
监听器的一些默认值:
Watch 用法2:绑定方法
<body>
<div id="root2">
<h3>Watch 用法2:绑定方法</h3>
<input v-model="message">
<span>{{copyMessage}}</span>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#root2',
watch: {
message: 'handleMessage'
},
data() {
return {
message: 'Hello Vue',
copyMessage: ''
}
},
methods: {
handleMessage(value) {
this.copyMessage = value
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
键为message,值为’handleMessage()方法,每次监听到message变化,’handleMessage()方法就会执行一次
PS:双向绑定的值(
v-model="message"和data() {return {message}})和watch监听的键要保持一致,同为message
Watch 用法3:deep + handler
<body>
<div id="root3">
<h3>Watch 用法3:deep + handler</h3>
<input v-model="deepMessage.a.b">
<span>{{copyMessage}}</span>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#root3',
watch: {
deepMessage: {
handler: 'handleDeepMessage',
deep: true
}
},
data() {
return {
deepMessage: {
a: {
b: 'Deep Message'
}
},
copyMessage: ''
}
},
methods: {
handleDeepMessage(value) {
this.copyMessage = value.a.b
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
默认情况下 watch方法只监听data中的对象,而无法监听到对象内部属性的改变,此时就需要deep属性对对象进行深度监听。(默认:deep:false)
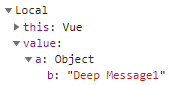
这个案例可以看出:双向绑定的值(v-model="deepMessage.a.b"和deepMessage:{a: {b:'Deep Message'}},)保持一致;watch不能直接监听deepMessage.a.b,而是需要通过handler和deep属性来完成监听
Watch 用法4:immediate
<body>
<div id="root">
<div id="root4">
<h3>Watch 用法4:immediate</h3>
<input v-model="message">
<span>{{copyMessage}}</span>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#root4',
watch: {
message: {
handler: 'handleMessage',
immediate: true,
}
},
data() {
return {
message: 'Hello Vue',
copyMessage: ''
}
},
methods: {
handleMessage(value) {
this.copyMessage = value
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
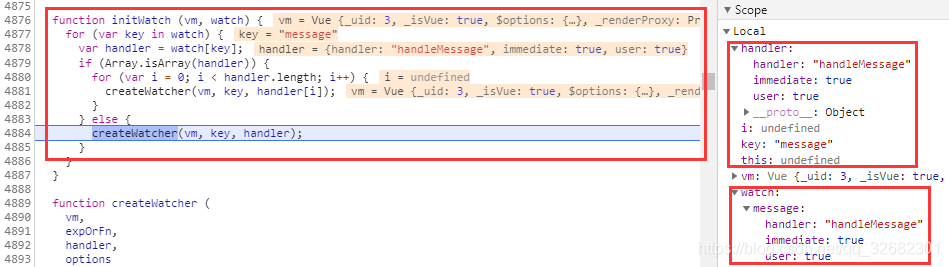
watch默认情况下在页面首次渲染时,即使监听的值有初始值,也不会直接执行,这种情况下想要第一次渲染后直接监听就需要添加属性:immediate: true
initWatch
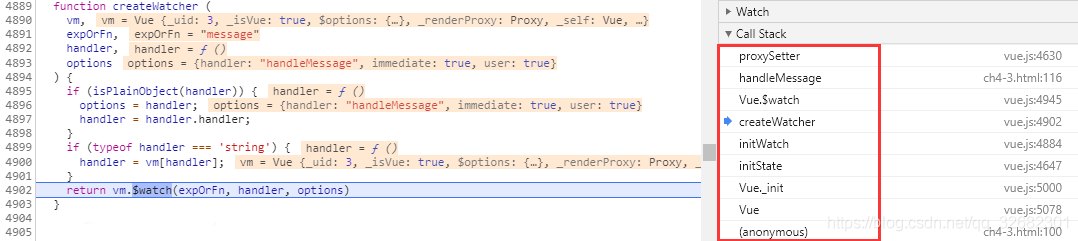
createWatch
Watch 用法5:绑定多个 handler
<body>
<div id="root5">
<h3>Watch 用法5:绑定多个 handler</h3>
<input v-model="message">
<span>{{copyMessage}}</span>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#root5',
watch: {
message: [{
handler: 'handleMessage',
},
'handleMessage2',
function(value) {
this.copyMessage = this.copyMessage + '...'
}]
},
data() {
return {
message: 'Hello Vue',
copyMessage: ''
}
},
methods: {
handleMessage(value) {
this.copyMessage = value
},
handleMessage2(value) {
this.copyMessage = this.copyMessage + '*'
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
监听值为多个,需要用数组形式:
- 值为对象:执行对象的handler属性值对应方法handleMessage
- 值为字符串:执行字符串对应方法handleMessage2
- 值为方法:直接执行方法
先监听的先执行,各自独立,每个都是独立的监听器
本示例中value都是一致的,只有handleMessage获取了这个value,其他监听器处理的都是上一步处理过的copyMessage
若多个监听器监听同一个对象,那么只会渲染最后一次处理结果
Watch 用法6:监听对象属性
<body>
<div id="root6">
<h3>Watch 用法6:监听对象属性</h3>
<input v-model="deepMessage.a.b">
<span>{{copyMessage}}</span>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#root6',
watch: {
'deepMessage.a.b': 'handleMessage'
},
data() {
return {
deepMessage: { a: { b: 'Hello Vue' } },
copyMessage: ''
}
},
methods: {
handleMessage(value) {
this.copyMessage = value
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
只监听对象的某少数个属性值时,可以用对象.属性字符串形式进行监听
Vue.js 源码分析(七) 基础篇 侦听器 watch属性详解
四、class 和 style 绑定的高级用法
<body>
<div id="root">
<div :class="['active', 'normal']">数组绑定多个class</div>
<div :class="[{active: isActive}, 'normal']">数组包含对象绑定class</div>
<div :class="[showWarning(), 'normal']">数组包含方法绑定class</div>
<div :style="[warning, bold]">数组绑定多个style</div>
<div :style="[warning, mix()]">数组包含方法绑定style</div>
<div :style="{ display: ['-webkit-box', '-ms-flexbox', 'flex'] }">style多重值</div>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#root',
data() {
return {
isActive: true,
warning: {
color: 'orange'
},
bold: {
fontWeight: 'bold'
}
}
},
methods: {
showWarning() {
return 'warning'
},
mix() {
return {
...this.bold,
fontSize: 20
}
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
数组绑定多个class
:class="'active normal'"
:class="'active'+'normal'"
:class="['active', 'normal']" // 更灵活
- 1
- 2
- 3
数组包含对象绑定class
:class="[{active: isActive}, 'normal']" // 老写法:class="(isActive?'active':'') + 'normal'"
- 1
数组包含方法绑定class
:class="[showWarning(), 'normal']"
- 1
数组绑定多个style
:style="[warning, bold]" // 这里的每个数组元素都是对象而不是字符串
- 1
数组包含方法绑定style
:style="[warning, mix()]"
- 1
style多重值
:style="{display:['-webkit-box','-ms-flexbox','flex']}"//从后往前,兼容哪个匹配哪个
- 1
五、Vue2.6 新特性
1.Vue.observable
<body>
<div id="root">
{{message}}
<button @click="change">Change</button>
</div>
<script>
const state = Vue.observable({ message: 'Vue 2.6' })
const mutation = {
setMessage(value) {
state.message = value
}
}
new Vue({
el: '#root',
computed: {
message() {
return state.message
}
},
methods: {
change() {
mutation.setMessage('Vue 3.0')
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
官方解释:
Vue.observable(object) 是vue2.6版本新增的全局API,它可以让一个对象可响应。Vue 内部会用它来处理 data 函数返回的对象。
返回的对象可以直接用于渲染函数和计算属性内,并且会在发生改变时触发相应的更新。也可以作为最小化的跨组件状态存储器,用于简单的场景
在 Vue 2.x 中,被传入的对象会直接被 Vue.observable 改变;在 Vue 3.x 中,则会返回一个可响应的代理,而对源对象直接进行修改仍然是不可响应的。因此,为了向前兼容,官方推荐始终操作使用 Vue.observable 返回的对象,而不是传入源对象。
通俗来说,Vue.observable在简单场景下可以代替vuex
本示例中Vue.observable执行流程:
- 首先initGlobalAPI (vue.js:5406)
- 执行Vue.observable内容
// 2.6 explicit observable API
Vue.observable = function (obj) {
observe(obj);
return obj
};
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- vue初始化
- 使用计算属性将state.message渲染到页面
- 点击按钮
- 执行change()
- 执行setMessage(),修改state.message的值
- 使用计算属性将新的state.message值渲染到页面
可以看出Vue.observable实际就是封装了observe:
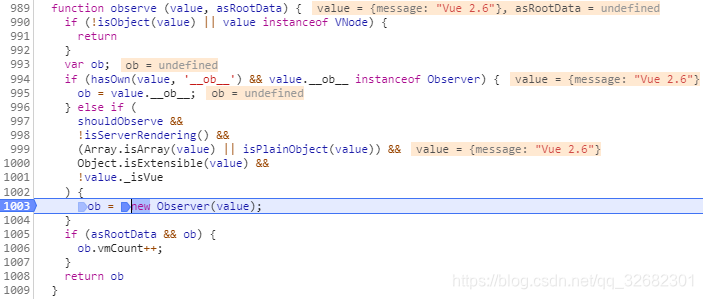
- 首先判断是否包含__ob__这个属性
- 实例化一个Observer对象:
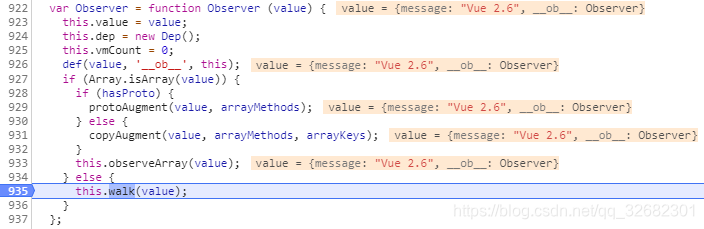
- 由于本实例中传入的不是数组,进入walk()
- 在walk中遍历key,并使用defineReactive$$1创建响应式对象
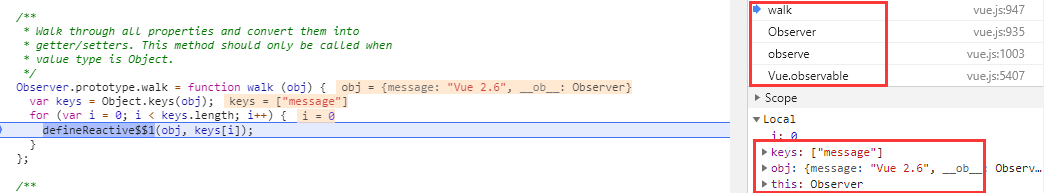
Walk through all properties and convert them into getter/setters. This method should only be called when value type is Object.
遍历所有属性并将它们转换为getter/setter。仅当值类型为Object时才应调用此方法。
- 通过property.get进行取值,通过property.set进行赋值

- 接下来调用Object.defineProperty()给对象定义响应式属性(Object.defineProperty是vue.js实现「响应式系统」的关键之一)
- enumerable,属性是否可枚举,默认 false。
- configurable,属性是否可以被修改或者删除,默认 false。
- get,获取属性的方法。(进行依赖收集)(数据劫持)
- set,设置属性的方法。(进行响应式更新)
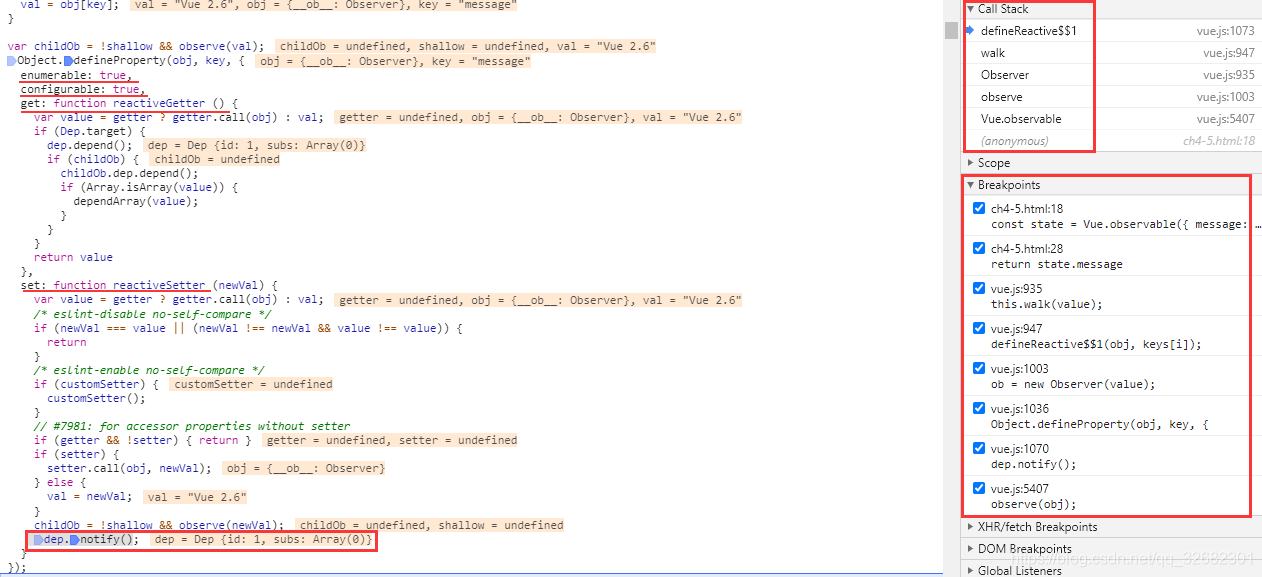
- dep.notify():通过dep.notify()对观察者watchers进行通知
- 然后state就成全局响应式对象了,
拓展:
- 深入响应式原理 — Vue.js
- vue原理探索–响应式系统
- Vue setter/getter 是何原理?
- 深入解析Vue依赖收集原理
- Vue 核心之数据劫持
- Vue源码解读之Dep,Observer和Watcher
思想来源:观察者模式 vs 发布订阅模式
2.插槽 slot
官方文档:https://cn.vuejs.org/v2/guide/components.html#通过插槽分发内容
官方文档:https://cn.vuejs.org/v2/guide/components-slots.html
官方文档:https://cn.vuejs.org/v2/api/#v-slot
实例:插槽 slot
<body>
<div id="root">
<div>案例1:slot的基本用法</div>
<Test>
<template v-slot:header="{user}">
<div>自定义header({{user.a}})</div>
</template>
<template v-slot="{user}">
<div>自定义body({{user.b}})</div>
</template>
</Test>
</div>
<div id="root2">
<div>案例2:Vue2.6新特性 - 动态slot</div>
<Test>
<template v-slot:[section]="{section}">
<div>this is {{section}}</div>
</template>
</Test>
<button @click="change">switch header and body</button>
</div>
<script>
Vue.component('Test', {
template:
'<div>' +
'<slot name="header" :user="obj" :section="\'header\'">' +
'<div>默认header</div>' +
'</slot>' +
'<slot :user="obj" :section="\'body\'">默认body</slot>' +
'</div>',
data() {
return {
obj: { a: 1, b: 2 }
}
}
})
new Vue({ el: '#root' })
new Vue({
el: '#root2',
data() {
return {
section: 'header'
}
},
methods: {
change() {
this.section === 'header' ?
this.section = 'default' :
this.section = 'header'
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
渲染结果:
<div id="root">
<div>案例1:slot的基本用法</div>
<div>
<div>自定义header(1)</div>
<div>自定义body(2)</div>
</div>
</div>
<div id="root2">
<div>案例2:Vue2.6新特性 - 动态slot</div>
<div>
<div>this is header</div>
默认body
</div>
<button>switch header and body</button>
</div>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
案例1中:
- 带有
name="header"的插槽为具名插槽,在案例中绑定了两个变量,变量user是组件的data中定义的对象obj,变量section是字符串'header' - 不带name属性的插槽为匿名插槽(也叫默认插槽default),在案例中绑定了两个变量,变量
user是组件的data中定义的对象obj,变量section是字符串'body' - 使用
组件Test和template标签引入插槽(v-slot只能用在component和template上)
PS:
- 插槽
slot不能直接获取当前vue实例的数据,只能获取定义插槽时绑定的数据- 匿名插槽,之前为
slot-scope="{user}",新写法写全了是v-slot:default="{user}",省略写法为v-slot:"{user}"或v-slot="{user}"v-slot可简写为#
案例2中:
v-slot:[section]="{section}"是动态插槽,section默认为#root2的data中定义的'header'- 点击按钮便可调用
change()方法,切换section的值,然后两个插糟的位置就会相互交换
其他用法可参考如下:
- 传送门 => vue 2.6 插槽更新 v-slot 用法总结
- 传送门 => Vue.js 你需要知道的 v-slot
- https://github.com/vuejs/rfcs/blob/master/active-rfcs/0001-new-slot-syntax.md
- 可利用动态插槽作为开关事件,切换 隐藏状态 或是 元素位置 等
PS:developer tool 断点调试小技巧
- Call Stack:显示当前断点的环境调用栈
- Breakpoints:当前js断点列表,添加的每个断点都会出现在此处,点击列表中断点就会定位到内容区的断点上
- DOM Breakpoints:当前DOM断点列表列表
- XHR Breakpoints:当前xhr断点列表,可点击右侧+添加断点
- Event Listener Breakpoints:事件监听器断点设置处
- Event Listeners:当前事件监听断点列表

评论(0)